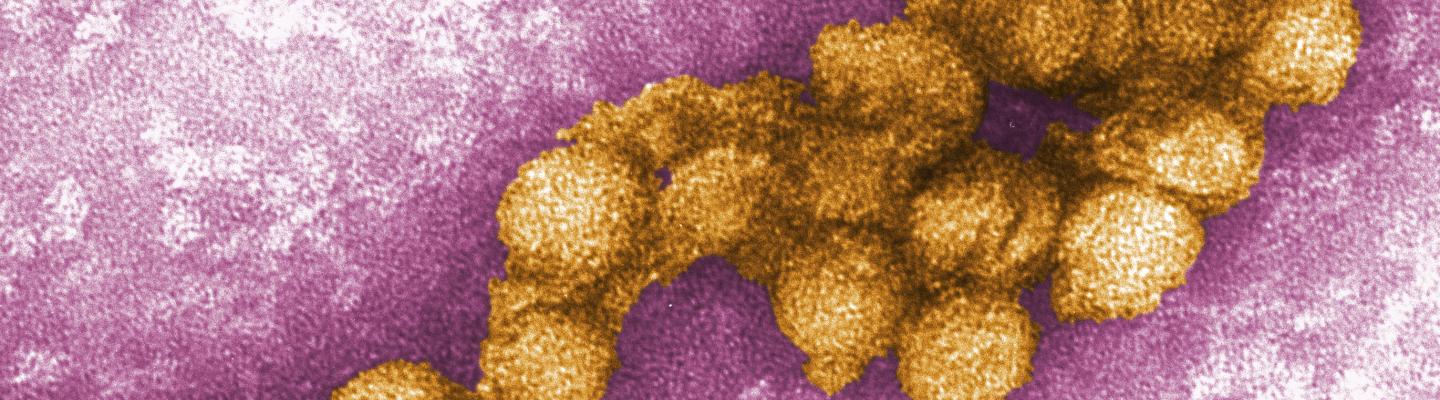
NIAID conducts and funds basic and clinical research on
- West Nile Virus (WNV) biology and viral structure
- Ways the virus causes human disease and persists in the body
- Viral interaction with and transmission among humans, birds, and mosquitoes
- Processes underlying WNV emergence and ecological patterns in the United States
- Insecticide resistance
With NIAID support in 2001 and 2002, researchers found that hamsters and mice are good models for WNV in humans. As a result, golden hamsters and mice are now used to test the efficacy of WNV vaccine candidates and antiviral treatments. NIAID-supported researchers are studying the different ways the immune system responds to WNV and how these responses interact to affect infection. Scientists are also examining how WNV evolves and adapts to changing environments and the structural changes that occur to the virus when it replicates.
NIAID has long supported the World Reference Center for Emerging Viruses and Arboviruses (WRCEVA), located at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston, which helps support research and outbreak investigations throughout the world. In response to the 2012 WNV outbreak in the United States, WRCEVA scientists sequenced several newly isolated WNV strains from Texas. Using genetic analysis, they compared different WNV strains to see if the virus has changed over time. In addition, the center has long provided research resources, such as viral isolates and reagents, to the scientific community. The center’s repository currently includes more than 500 WNV strains and isolates from across the globe.
In July 2012, in a NIAID-supported observational study of WNV patients in the Houston area, researchers at the Baylor College of Medicine discovered chronic kidney disease among 40 percent of patients long after recovery from acute disease. The study highlights the continuing need to investigate the pathology behind persistent infections, clinical outcomes, and treatment options.
Scientific Advances
Scientists Discuss Prototype Pathogens for Pandemic Preparedness
October 19, 2023A special Oct. 19 supplement to the Journal of Infectious Diseases contains nine articles intended as a summary of a National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID)-hosted pandemic preparedness workshop that featured scientific experts on viral families of pandemic concern.
World Mosquito Day 2023—How Mathematical Modeling Reveals the Link Between Climate Change and Mosquito-Borne Diseases
August 18, 2023As global temperatures rise, it has become more urgent to understand the interactions between climate, mosquitoes, and the pathogens mosquitoes transmit to humans. NIAID Now spoke to Luis Chaves, Ph.D., a 2023 Scholar with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Climate Change and Health Initiative, about his work about the impacts of environmental change on the ecology of insect vectors and the…

Cornell Professor—Environment Drives Mosquito-borne Diseases
August 19, 2022In recognition of World Mosquito Day on Saturday, Aug. 20, NIAID interviewed grantee Courtney Murdock, Ph.D., of Cornell University to learn more about her team’s research on the relationship between the environment and mosquito-borne diseases. Read how monitoring temperature, humidity – and the need for more data – will affect whether scientists can make a significant public health impact for…