57 Results
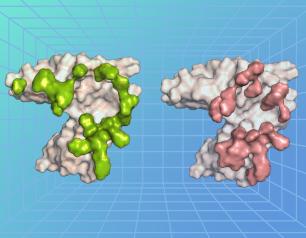
Epstein-Barr Virus’s Molecular Mimicry Reveals a Key Site of Vulnerability
NIAID scientists determined the high-resolution 3D structure of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) surface protein in complex with its receptor, revealing a key site of vulnerability that could lead to much-needed interventions against this common human pathogen.
Measuring Innovation: Laboratory Infrastructure to Deliver Essential HIV Clinical Trial Results
HIV clinical trials network laboratory functions will continue to evolve to align with scientific priorities and research approaches.
NIAID Research Key to H5N1 Influenza Preparedness Efforts
H5N1 influenza viruses have been around for years, but the spring 2024 outbreak of a highly pathogenic H5N1 avian influenza among U.S. dairy cows prompted new concerns. NIAID scientists and NIAID-funded researchers have been working closely to monitor the outbreak, understand spread among animals and develop potential prevention and treatment methods as part of larger U.S. government pandemic preparedness efforts.

Next-generation Genetic Tools Reveal New Aspects of Enterovirus Evolution
NIAID scientists developed tools to study evolution in enteroviruses—a virus group responsible for polio; hand, foot & mouth disease (HFMD); acute flaccid myelitis (AFM) & other diseases. Their findings may reveal pathways of viral evolution.
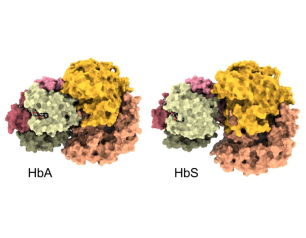
A New View of Hemoglobin and its Role in Malaria
A look inside human arteries reveals a new picture of hemoglobin’s role there and may lead to treatments for malaria and other vascular diseases.
First Webinar of Long COVID Treatment Initiative Highlights Early Progress
NIAID and the Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (FNIH) launched its first in a series of online webinars highlighting recent progress in the new Researching COVID to Enhance Recovery - Treating Long COVID (RECOVER-TLC) program.
Shaping the Next Era of HIV Therapeutics and Care
The Institute aims to foster the next generation of discoveries that will enable people with HIV to experience a typical lifespan with high life quality. Scientific priorities include removing the chronic HIV medication burden; reducing the incidence of concurrent TB and hepatitis; and ensuring scientific advances can feasibly be scaled to all who stand to benefit.
Can Improved Tests Speed Up Treatment for Antibacterial Resistant Infections?
An ongoing NIAID-supported trial is testing whether rapid tests for antibiotic susceptibility can improve patient outcomes.
Sequencing of Congo Mpox Reports Highlights New Transmission Patterns in Country
Laboratory analysis in the Republic of Congo showed mpox was affecting people in parts of the country where it has not been historically. The findings point to increases in human-to-human transmission across the border with the neighboring Democratic Republic of the Congo, where a large outbreak was declared a public health emergency of international concern.
HIVR4P 2024 Research Highlights: Reproductive Health While on PrEP and Signals to Guide HIV Vaccines and Cure
New NIAID-supported science presented at the 2024 HIV Research for Prevention conference in Lima, Peru features a breadth of HIV discovery and translational findings and enriches the evidence base on HIV pre-exposure prophylaxis within the context of reproductive health.
COVID-19 Respiratory Treatment Effective in Encephalitis Study
Antiviral drug molnupiravir, a COVID-19 treatment, was effective when tested in mice in preventing viruses that cause brain swelling, particularly in children. The scientists studied LACV because it broadly represents several RNA viruses that cause disease in the CNS, including Jamestown Canyon and Cache Valley viruses – which also were part of the study – and rabies, polio, West Nile, Nipah and several other viruses not part of the study.
Defining the Goals of HIV Science Through 2034
Discovery, Development and Delivery for an Increasingly Interconnected HIV Landscape
By Carl Dieffenbach, Ph.D., director, Division of AIDS, NIAID
We envision an HIV research enterprise that follows a logical evolution in addressing new scientific priorities informed by previous research progress. We will fund our next networks to align with updated research goals to take us through the end of 2034. Our capacity must reflect an increasing interdependence across clinical practice areas and public health contexts.
Study Links Certain Vaginal Bacteria and Inflammatory Marker to Increased Odds of Acquiring HIV Among Cisgender Women
Fourteen vaginal bacterial species and the presence of a protein that promotes inflammation were associated with increased odds of HIV acquisition in a study of more than 500 cisgender women in African countries with high HIV incidence. The study was the largest to date to prospectively analyze the relationship between both the vaginal microbiome and vaginal tissue inflammation and the likelihood of acquiring HIV among cisgender women in this population.
NIAID Funds Cutting-Edge Genomics and Bioinformatics Programs
NIAID has announced six awards to continue the Genomics Centers for Infectious Diseases (GCIDs) and Bioinformatics Resource Centers (BRCs) for Infectious Diseases, both important data science networks offering critical resources for the scientific community.

Charting the Path to an HIV-Free Generation
NIAID supports four research networks as part of its HIV clinical research enterprise. Every seven years, the Institute engages research partners, community representatives, and other public health stakeholders in a multidisciplinary evaluation of network progress toward short- and long-term scientific goals. Pregnancy, childbirth and the postnatal period are a key focus of NIAID HIV research and call for measures to support the health of people who could become pregnant as well as their infants.
Our Words Have Power—NIAID Embraces Respectful, Inclusive, and Person-First Language
by Jeanne Marrazzo, M.D., M.P.H., NIAID Director
Our institute is responsible not only for advancing scientific knowledge, but for doing so in a way that honors the dignity, individuality, and autonomy of the people affected by the health issues we address. For this reason, I am very proud to share the updated NIAID HIV Language Guide, a thoroughly vetted resource to inform our written and verbal communications.
Stepping into Science
Realizing that traditional laboratory science – aka “bench research” – isn’t for everyone, staff at NIAID's Rocky Mountain Laboratories recently invited two dozen area high school students to experience not only traditional research but also the lesser-known careers that make bench research possible.
Antiretroviral Drug Improves Kidney Function After Transplant in People with HIV
An HIV drug that suppresses the activity of the CCR5 receptor—a collection of proteins on the surface of certain immune cells—was associated with better renal function in kidney transplant recipients with HIV compared to people who took a placebo in a randomized trial. According to the authors, these findings warrant further exploration of the benefit of CCR5 antagonists in all kidney transplant recipients regardless of HIV status. The findings of the NIAID-sponsored trial were presented today at the 2024 American Transplant Congress in Philadelphia.
Proof-of-Concept Study Shows an HIV Vaccine Can Generate Key Antibody Response in People
An HIV vaccine candidate elicited trace levels of HIV broadly neutralizing antibodies and high levels of other key immune cells in an early-stage clinical trial. This immune response is an important signal that, if antibody levels can be further amplified, the vaccination strategy might be able to prevent HIV.
NIAID Marks HIV Vaccine Awareness Day 2024
On the 27th observance of HIV Vaccine Awareness Day (Saturday, May 18), we express our gratitude to the dedicated global community of scientists, advocates, study participants, study staff, and funders working toward a safe, effective, durable, and accessible HIV vaccine.

Exploring a Meningitis Vaccine for Gonorrhea Prevention
A preventive vaccine for gonorrhea would be a major advance in public health, according to an editorial co-authored by NIAID Director Jeanne Marrazzo. The genetic sequences of the bacteria that cause gonorrhea and meningitis B, are closely related. This has led researchers to explore whether the 4CMenB vaccine, approved by the Food and Drug Administration for meningitis B, might also prevent gonorrhea. NIAID is sponsoring an efficacy study of the 4CMenB vaccine for gonorrhea prevention.
Making an Impact: Results from an NIAID-funded Study of Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients
Why do some people hospitalized with COVID-19 succumb, while others—with apparently similar disease severity at the time of hospitalization—survive? Among older individuals, are there particular immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 virus infection that set the stage for the increased risk of severe COVID-19? New publications from the NIAID-funded IMPACC study help provide answers.
New Tool Identifies Aedes Mosquito Exposure in People
Scientists at NIAID developed a new tool to help identify geographic hot spots for Aedes mosquitoes, a type of mosquito that can spread diseases such as dengue, Zika and chikungunya. The tool uses a marker from blood serum to identify people bitten by Aedes mosquitoes. Monitoring for this marker in blood samples could help find sites where disease-carrying mosquitoes live, allowing for targeted interventions against dengue and other diseases.
The HIV Field Needs Early-Stage Investigators (VIDEO)
by Jeanne Marrazzo, M.D., M.P.H., NIAID Director
The HIV research community is led by scientists with deep personal commitments to improving the lives of people with and affected by HIV. Our collective decades of work have generated HIV testing, prevention and treatment options beyond what we could have imagined in the 1980s. Those advances enable NIAID to explore new frontiers: expanding HIV prevention and treatment modalities, increasing understanding of the interplay between HIV and other infectious and non-communicable diseases, optimizing choice and convenience, and building on the ever-growing knowledge base that we need to develop a preventive vaccine and cure. The next generation of leaders will bring these concepts to fruition, and we need to welcome and support them into the complex and competitive field of HIV science.
Sexually Transmitted Infections—A Closer Look at NIAID Research
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites. NIAID supports research across the spectrum from basic to clinical science to develop effective diagnostic, preventive and therapeutic approaches to STIs in alignment with the National STI Strategic Plan. In recognition of National STI Awareness Week, NIAID shares a snapshot of new projects and recent scientific advances in STI research.


