12 Results
Powerful Sequencing Tool Helps Identify Infectious Diseases in Mali
Advanced diagnostic tool tested in Mali helped identify infectious viruses in patients that normally would have required many traditional tests.

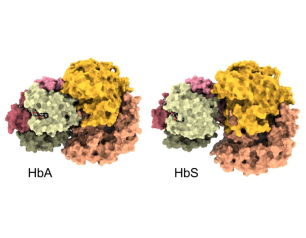
A New View of Hemoglobin and its Role in Malaria
A look inside human arteries reveals a new picture of hemoglobin’s role there and may lead to treatments for malaria and other vascular diseases.
World Mosquito Day 2024—The Metabolic Mysteries of Mosquito Metabolism
Mosquitoes are considered one of the most dangerous animals on earth because of their broad distribution and the many pathogens they transmit to humans. Dr. Patricia Scaraffia, Associate Professor at the Tulane University School of Public Health and Tropical Medicine, has dedicated her career to understanding the metabolism of the mosquito species that carries the pathogens responsible for dengue, Zika, chikungunya, and yellow fever to humans. NIAID reached out to Dr. Scaraffia about her team’s research.

The Hidden Link Between Malaria and Lupus
Scientists have long been aware that malaria infection is associated with high levels of autoantibodies—antibodies that recognize and attack the person’s own tissues and are associated with autoimmune disorders. NIAID researchers, along with their colleagues, have studied the molecular mechanisms of these autoantibodies. Their findings reveal the associations between malaria, human resistance to it, and autoantibodies that are linked to certain autoimmune disorders—specifically, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).
NIAID Raises Awareness to Malaria-like Diseases in W. Africa
NIAID scientists and colleagues have identified dengue, Zika and chikungunya viruses in the West African country of Mali, where health care providers could be misdiagnosing patients as having malaria. All four infectious diseases are caused by a mosquito bite.
NIAID Commemorates World Malaria Day 2024
Malaria, the fifth most deadly infectious disease, remains a public health priority. On April 25, World Malaria Day, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), joins with the global health community in reaffirming our commitment to ending this ancient parasitic disease. This year’s theme, “Accelerating the fight against...
Building a Better Malaria Vaccine—NIAID Researchers Design a Paradigm-Busting Candidate
NIAID researchers used structural information about two malaria parasite proteins along with mechanistic information about the interaction between them to design and build an entirely novel candidate vaccine. When tested in rats, their “structure-based design 1” (SBD1) immunogen vaccine performed better than other experimental malaria vaccines. It also upends the conventional wisdom that successful vaccines must elicit receptor-blocking antibodies.
NIAID Researchers Study Causes of Brain Swelling in Cerebral Malaria
In children with cerebral malaria, brain swelling can cause seizures, coma, and death. Researchers from NIAID and their colleagues studied children with cerebral malaria in Malawi to better understand the underlying causes of these devastating symptoms.
NIAID-Funded Study Traces Evolution of Malaria Drug Resistance in E. Africa
A new NIAID-funded study shows how inconsistent malaria control measures in East Africa could be aiding the emergence of drug-resistant mutations in the primary parasite that causes malaria.

World Mosquito Day 2023—How Mathematical Modeling Reveals the Link Between Climate Change and Mosquito-Borne Diseases
As global temperatures rise, it has become more urgent to understand the interactions between climate, mosquitoes, and the pathogens mosquitoes transmit to humans. NIAID Now spoke to Luis Chaves, Ph.D., a 2023 Scholar with the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Climate Change and Health Initiative, about his work about the impacts of environmental change on the ecology of insect vectors and the diseases they transmit.

NIAID’s VRC, S. Africa’s Afrigen Kick Off Vaccine-Sharing Efforts
A team of vaccine production experts from South Africa recently finished training with NIAID Vaccine Research Center scientists. Their objective: to globally produce vaccines against a list of troubling infectious diseases.

Promising Advances for Antibody Treatment of Viruses that Cause Neurologic and Arthritic Diseases
NIAID scientists and colleagues are one step closer to developing a safe and effective therapy against alphaviruses, which are spread by mosquitoes and can cause two types of disease in people: causing severe neurological impairment such as encephalitis (brain swelling) or crippling muscle pain similar to arthritis.


