Study Provided Data for Clinical Testing to Commence
May 15, 2020
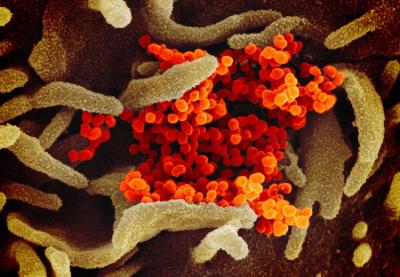
This scanning electron microscope image shows SARS-CoV-2 (orange)—also known as 2019-nCoV, the virus that causes COVID-19—isolated from a patient in the U.S., emerging from the surface of cells (green) cultured in the lab. Image captured and colorized at NIAID's Rocky Mountain Laboratories (RML) in Hamilton, Montana.
A single dose of ChAdOx1 nCoV-19, an investigational vaccine against SARS-CoV-2, has protected six rhesus macaques from pneumonia caused by the virus, according to National Institutes of Health scientists and University of Oxford collaborators. SARS-CoV-2 is the virus that causes COVID-19. The researchers posted their data to the preprint server bioRxiv. The findings are not yet peer-reviewed but are being shared to assist the public health response to COVID-19. Based on these data, a Phase 1 trial of the candidate vaccine began on April 23 in healthy volunteers in the United Kingdom.
The vaccine was developed at the University of Oxford Jenner Institute. It uses a replication-deficient chimpanzee adenovirus to deliver a SARS-CoV-2 protein to induce a protective immune response. ChAdOx1 has been used to develop investigational vaccines against several pathogens, including a closely related coronavirus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). The scientists quickly adapted the platform to SARS-CoV-2 when the first cases of COVID-19 emerged. They showed that the vaccine rapidly induced immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 in mice and rhesus macaques. They then conducted vaccine efficacy testing on the macaques at NIAID’s Rocky Mountain Laboratories (RML) in Hamilton, Montana. Six animals that received the investigational vaccine 28 days before being infected with SARS-CoV-2 were compared with three control animals that did not receive the vaccine. The vaccinated animals showed no signs of virus replication in the lungs, significantly lower levels of respiratory disease and no lung damage compared to control animals.
Oxford University has entered into a partnership with UK-based global biopharmaceutical company AstraZeneca for the further development, large-scale manufacture and potential distribution of the vaccine.
ARTICLE:
N van Doremalen et al. Single dose ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 vaccination reduces SARS-CoV-2 replication and prevents pneumonia in rhesus macaques.
WHO:
Vincent Munster, Ph.D., chief of the Virus Ecology Unit in NIAID’s Laboratory of Virology, is available to comment on this study.
Contact
To schedule interviews, contact:
NIAID Office of Communications
(301) 402-1663
NIAIDNews@niaid.nih.gov

