131 Results
NIH Study Finds Tecovirimat Was Safe but Did Not Improve Mpox Resolution or Pain
December 10, 2024
Tecovirimat was safe but did not reduce the time to lesion resolution or reduce pain among adults with mild to moderate clade II mpox and a low risk of severe disease in an international study.
Statement—Large NIH Clinical Trial Will Test Polyclonal Antibody Therapeutic for COVID-19
April 21, 2021
A Phase 2/3 trial to evaluate a new fully-human polyclonal antibody therapeutic targeted to SARS-CoV-2, called SAB-185, has begun enrolling non-hospitalized people with mild or moderate cases of COVID-19. The trial, ACTIV-2, is sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. The therapeutic was developed by SAB Biotherapeutics, Inc. (Sioux Falls, South Dakota).
Experimental mRNA HIV Vaccine Safe, Shows Promise in Animals
December 9, 2021
An experimental HIV vaccine based on mRNA—the same platform technology used in two highly effective COVID-19 vaccines—shows promise in mice and non-human primates, according to scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.
World TB Day 2023 – ‘Yes! We Can End TB!’
March 24, 2023
Each year, on March 24, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the NIH, joins people and organizations from around the globe in marking World Tuberculosis Day. On this day, more than 140 years ago, Dr. Robert Koch announced his discovery that most human tuberculosis (TB) is caused by the bacterium Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb). Although our scientific insight into this disease has grown over the past century, TB is still one of the deadliest infectious diseases on the planet. Today, NIAID joins the world in a message of hope: “Yes!
The Antiviral Tecovirimat is Safe but Did Not Improve Clade I Mpox Resolution in Democratic Republic of the Congo
August 15, 2024
The antiviral drug tecovirimat did not reduce the duration of mpox lesions among children and adults with clade I mpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), based on an initial analysis of data from a randomized, placebo-controlled trial.
Statement—Janssen Investigational COVID-19 Vaccine—Interim Analysis
January 29, 2021
NIH reports that an investigational COVID-19 vaccine by Janssen Pharmaceuticals appears to be safe and effective at preventing COVID-19 in adults.
HIV Vaccine Candidate Does Not Sufficiently Protect Women Against HIV Infection
August 31, 2021
An investigational HIV vaccine tested in the “Imbokodo” clinical trial conducted in sub-Saharan Africa posed no safety concerns but did not provide sufficient protection against HIV infection, according to a primary analysis of the study data. The Phase 2b proof-of-concept study, which began in November 2017, enrolled 2,637 women ages 18 to 35 years from five countries.
NIH Experts Discuss SARS-CoV-2 Viral Variants
February 12, 2021
The rise of several significant variants of SARS-CoV-2 has attracted the attention of health and science experts worldwide, NIH reports.
Existing Drug Shows Promise as Treatment for Rare Genetic Disorder
May 30, 2024
A drug approved to treat certain autoimmune diseases and cancers successfully alleviated symptoms of a rare genetic syndrome called autoimmune polyendocrine syndrome type 1 (APS-1).
NIH Establishes New Childhood Asthma Clinical Research Network
April 23, 2021
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, has awarded $10 million in first-year funding to establish a clinical research network called Childhood Asthma in Urban Settings (CAUSE). This nationwide network will conduct observational studies and clinical trials to improve understanding of asthma and develop treatment and prevention approaches tailored to children of low-income families living in urban communities. NIAID intends to provide approximately $70 million over seven years to support the CAUSE network.
NIH Launches Clinical Trial of mRNA Nipah Virus Vaccine
July 11, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases has launched an early-stage clinical trial evaluating an investigational vaccine to prevent infection with Nipah virus.
NIH Launches Clinical Trial of Epstein-Barr Virus Vaccine
May 6, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, has launched an early-stage clinical trial to evaluate an investigational preventative vaccine for Epstein-Barr virus (EBV). EBV is the primary cause of infectious mononucleosis and is associated with certain cancers and autoimmune diseases. The Phase 1 study, which will be conducted at the NIH Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland, is one of only two studies to test an investigational EBV vaccine in more than a decade.
Vaccine-Induced Immune Response to Omicron Wanes Substantially Over Time
July 19, 2022
Although COVID-19 booster vaccinations in adults elicit high levels of neutralizing antibodies against the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2, antibody levels decrease substantially within 3 months, according to new clinical trial data. The findings, published today in Cell Reports Medicine, are from a study sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. The trial was led by NIAID’s Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Consortium.
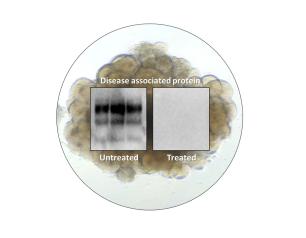
NIH Scientists Use Human Cerebral Organoid to Test Drug for Deadly Brain Disease
March 9, 2021
After establishing a human cerebral organoid system to study CJD, NIAID researchers have developed the model to screen drugs for potential CJD treatment.
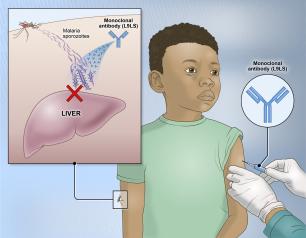
Experimental NIH Malaria Monoclonal Antibody Protective in Malian Children
April 26, 2024
One injected dose of an experimental malaria monoclonal antibody was 77% effective against malaria disease in children in Mali during the country’s six-month malaria season, according to the results of a mid-stage clinical trial. The trial assessed an investigational monoclonal antibody developed by scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and results appear in The New England Journal of Medicine.
NIH Selects Dr. Jeanne Marrazzo as Director of the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
August 2, 2023
Lawrence A. Tabak, D.D.S., Ph.D., acting director for the National Institutes of Health (NIH), has named Jeanne M. Marrazzo, M.D., as director of NIH’s National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID).

Marburg Vaccine Shows Promising Results in First-in-Human Study
January 30, 2023
A newly published paper in The Lancet shows that an experimental vaccine against Marburg virus (MARV) was safe and induced an immune response in a small, first-in-human clinical trial. The vaccine, developed by researchers at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, could someday be an important tool to respond to Marburg virus outbreaks.
Topical Steroid Withdrawal Diagnostic Criteria Defined by NIH Researchers
March 14, 2025
Topical steroid withdrawal (TSW) results in dermatitis that is distinct from eczema and is caused by an excess of NAD+, an essential chemical compound in the body, according to a new study from NIAID researchers.
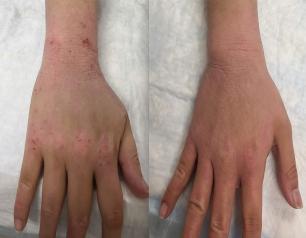
NIH Officials Assess Threat of H5N1
December 31, 2024
HPAI H5N1 influenza remains a low risk to most Americans, but that does not diminish concern about the virus, NIAID experts say.
NIAID Discovery Leads to Novel Probiotic for Eczema
June 26, 2024
NIAID research has led to the availability of a new over-the-counter topical eczema probiotic. The probiotic is based on the discovery by scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, that bacteria present on healthy skin called Roseomonas mucosa can safely relieve eczema symptoms in adults and children.
Mix-and-Match Trial Finds Additional Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine Safe, Immunogenic
January 26, 2022
In adults who had previously received a full regimen of any of three COVID-19 vaccines granted Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) or approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), an additional booster dose of any of these vaccines was safe and prompted an immune response, according to preliminary clinical trial results reported in The New England Journal of Medicine. The findings served as the basis for recommendations by the FDA and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention in late fall 2021 to permit mix-and-match COVID-19 booster vaccinations in the United States.
Infectious H5N1 Influenza Virus in Raw Milk Rapidly Declines with Heat Treatment
June 14, 2024
The amount of infectious H5N1 influenza viruses in raw milk rapidly declined with heat treatment in laboratory research conducted by scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health. However, small, detectable amounts of infectious virus remained in raw milk samples with high virus levels when treated at 72 degrees Celsius (161.6 degrees Fahrenheit) for 15 seconds—one of the standard pasteurization methods used by the dairy industry.

NIH Celebrates FDA Approval of RSV Vaccine for People 60 Years of Age and Older
May 4, 2023
Food and Drug Administration announced the approval of the first respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) vaccine approved for use in the United States. The vaccine, Arexvy, is approved for the prevention of lower respiratory tract disease caused by RSV in individuals 60 years of age and older.
NIH Scientists Find Weak Points on Epstein-Barr Virus
March 12, 2024
Studies of interactions between two lab-generated monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and an essential Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) protein have uncovered targets that could be exploited in designing treatments and vaccines for this extremely common virus. The research was led by Jeffrey I. Cohen, M.D., and colleagues from NIAID.

NIH Clinical Trial Evaluating Moderna COVID-19 Variant Vaccine Begins
March 31, 2021
An investigational vaccine designed to protect against the B.1.351 SARS-CoV-2 variant has been administered as part of a new Phase 1 clinical trial evaluating the vaccine candidate’s safety and immunogenicity in adult volunteers. The vaccine, known as mRNA-1273.351, was developed by the biotechnology company ModernaTX, Inc., based in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The trial is led and funded by NIAID. The trial will enroll approximately 210 healthy adult volunteers at four clinical research sites in the United States that are part of the NIAID-funded Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Consortium (IDCRC).

