131 Results
NIH Researchers Discover New Autoinflammatory Disease, Suggest Target for Potential Treatments
March 28, 2023
Scientists have identified an autoinflammatory disease caused by mutations in the LYN gene, an important regulator of immune responses in health and disease.
Intranasal Influenza Vaccine Spurs Strong Immune Response in Phase 1 Study
February 3, 2021
An experimental influenza vaccine was safe and produced a durable immune response when tested in a Phase 1 study, NIH reports.
NIH Scientists Develop Mouse Model to Study Mpox Virulence
February 14, 2023
Scientists from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, have removed a major roadblock to better understanding of mpox (formerly, monkeypox). They developed a mouse model of the disease and used it to demonstrate clear differences in virulence among the major genetic groups (clades) of mpox virus (MPXV). The research, appearing in Proceedings of the National Academy of Science, was led by Bernard Moss, M.D., Ph.D., chief of the Genetic Engineering Section of NIAID’s Laboratory of Viral Diseases.
NIH Awards $12 Million for Antiviral Therapeutic Development
November 21, 2022
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, recently awarded more than $12 million to three institutions for the development of antiviral therapies to treat diseases caused by viruses with pandemic potential.
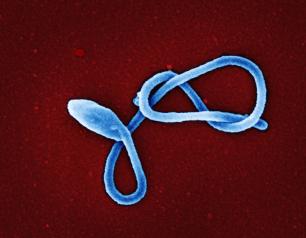
NIH Hamster Study Evaluates Airborne and Fomite Transmission of SARS-CoV-2
August 17, 2021
National Institutes of Health scientists studying SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, have defined in Syrian hamsters how different routes of virus exposure are linked to disease severity. Their study, published in Nature Communications, details the efficiency of airborne transmission between hamsters and examines how the virus replicates and causes disease throughout the respiratory system. Their work also shows that virus transmission via fomites—exposure from contaminated surface contact—is markedly less efficient than airborne transmission but does occur.
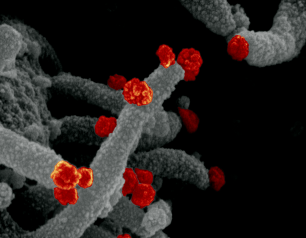
NIH Study Examines Connections Between Drinking Water Quality and Increased Lung Infections in People with Cystic Fibrosis
August 25, 2023
High levels of some minerals and metals in environmental water supplies may increase the risk of nontuberculous mycobacteria (NTM) pulmonary infections in people with cystic fibrosis. The study appearing in Environmental Epidemiology, found the presence of the metals molybdenum and vanadium along with sulfate—a collection of mineral salts—in the U.S. municipal water system was associated with an increased incidence of NTM pulmonary infections, the leading cause of drinking-water associated illnesses.
Media Availability—COVID Vaccine Booster Increases Antibody Responses, Is Protective in Rhesus Macaques
October 21, 2021
A booster dose of the mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccine given to rhesus macaques about six months after their primary vaccine series significantly increased levels of neutralizing antibodies against all known SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern, according to a new study from National Institutes of Health scientists and colleagues.

NIH Researchers Uncover New Details on Rare Immune Disease
May 3, 2023
In an 11-year study, researchers at the National Institutes of Health have further characterized idiopathic CD4 lymphocytopenia (ICL), a rare immune deficiency that leaves people vulnerable to infectious diseases, autoimmune diseases and cancers. Researchers observed that people with the most severe cases of ICL had the highest risk of acquiring or developing several of the diseases associated with this immune deficiency. This study, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, was led by Irini Sereti M.D., M.H.S. and Andrea Lisco, M.D., Ph.D.
Experimental Monoclonal Antibodies Show Promise Against Epstein-Barr Virus
October 27, 2022
A panel of investigational monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) targeting different sites of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) blocked infection when tested in human cells in a laboratory setting. Moreover, one of the experimental mAbs provided nearly complete protection against EBV infection and lymphoma when tested in mice. The results appear online in the journal Immunity.
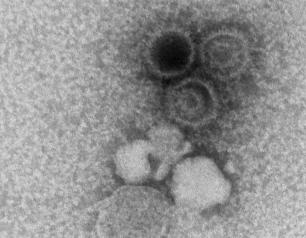
Lung Autopsies of COVID-19 Patients Reveal Treatment Clues
November 17, 2021
Lung autopsy and plasma samples from people who died of COVID-19 have provided a clearer picture of how the SARS-CoV-2 virus spreads and damages lung tissue.
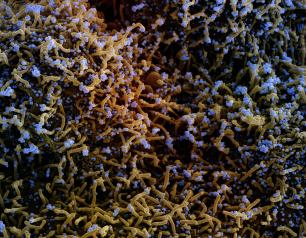
NIH Scientists Study Salmonella Swimming Behavior as Clues to Infection
January 13, 2021
NIH scientists believe they have identified a protein, that allows the Salmonella bacteria to swim straight when they are ready to infect cells.
NIH Releases Strategic Plan for Research on Herpes Simplex Virus 1 and 2
September 19, 2023
In response to the persistent health challenges of herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) and HSV-2, an NIH-wide HSV Working Group developed the plan, informed by feedback from more than 100 representatives of the research and advocacy communities and interested public stakeholders. The plan outlines an HSV research framework with four strategic priorities: improving fundamental knowledge of HSV biology, pathogenesis, and epidemiology; accelerating research to improve HSV diagnosis; improving strategies to treat HSV while seeking a curative therapeutic; and, advancing research to prevent HSV infection.

NIH Clinical Trial of Universal Flu Vaccine Candidate Begins
September 15, 2023
Enrollment in a Phase 1 trial of a new investigational universal influenza vaccine candidate has begun at the National Institutes of Health’s Clinical Center in Bethesda, Maryland. The trial is sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the NIH, and will evaluate the investigational vaccine for safety and its ability to elicit an immune response.
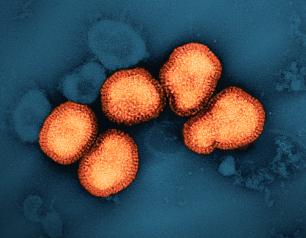
Experimental NIH Sudan Virus Vaccine Protects Macaques
February 2, 2023
A National Institutes of Health research group with extensive experience studying ebolavirus countermeasures has successfully developed a vaccine against Sudan virus (SUDV) based on the licensed Ebola virus (EBOV) vaccine. SUDV, identified in 1976, is one of the four viruses known to cause human Ebolavirus disease. The new vaccine, VSV-SUDV, completely protected cynomolgus macaques against a lethal SUDV challenge. The findings were published in the journal The Lancet Microbe.
NIAID Scientists Find a Key to Hepatitis C Entry into Cells
September 21, 2021
Understanding Structure of HCV Proteins Could Aid in Vaccine Development
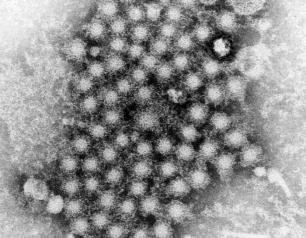
NIH Scientists Describe “Multi-Kingdom Dialogue” Between Internal, External Microbiota
June 23, 2021
National Institutes of Health scientists and their collaborators have identified an internal communication network in mammals that may regulate tissue repair and inflammation, providing new insights on how diseases such as obesity and inflammatory skin disorders develop.
Experimental Antiviral for COVID-19 Effective in Hamster Study
April 16, 2021
The experimental antiviral drug MK-4482 significantly decreased levels of virus and disease damage in the lungs of hamsters treated for SARS-CoV-2 infection, according to a new study from National Institutes of Health scientists. SARS-CoV-2 is the virus that causes COVID-19. MK-4482, delivered orally, is now in human clinical trials. Remdesivir, an antiviral drug already approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for use against COVID-19, must be provided intravenously, making its use primarily limited to clinical settings.
NIAID Issues New Awards to Fund “Pan-Coronavirus” Vaccines
September 28, 2021
The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, has awarded approximately $36.3 million to three academic institutions to conduct research to develop vaccines to protect against multiple types of coronaviruses and viral variants. The awards are intended to fuel vaccine research for a diverse family of coronaviruses, with a primary focus on potential pandemic-causing coronaviruses, such as SARS-CoV-2.
Single Mutation in H5N1 Influenza Surface Protein Could Enable Easier Human Infection
December 6, 2024
A single modification in the protein found on the surface of the highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI) H5N1 influenza virus currently circulating in U.S. dairy cows could allow for easier transmission among humans, according to new research funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and published today in the journal Science. The study results reinforce the need for continued, vigilant surveillance and monitoring of HPAI H5N1 for potential genetic changes that could make the virus more transmissible in humans.
Mpox Vaccine Is Safe and Generates a Robust Antibody Response in Adolescents
October 16, 2024
A clinical trial of an mpox vaccine in adolescents found it was safe and generated an antibody response equivalent to that seen in adults. Results were presented at IDWeek2024.
Findings Suggest COVID-19 Rebound Not Caused by Impaired Immune Response
October 6, 2022
Findings from a small study of eight patients published in Clinical Infectious Diseases suggest that COVID-19 rebound is likely not caused by impaired immune responses. The study, led by scientists at the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, aimed to define the clinical course and the immunologic and virologic characteristics of COVID-19 rebound in patients who have taken nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (Paxlovid), an antiviral therapeutic developed by Pfizer, Inc.
NIH Launches Trial to Study Allergic Reactions to COVID-19 mRNA Vaccine
March 9, 2022
Researchers from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) are conducting a clinical trial designed to help understand rare but potentially serious systemic allergic reactions to COVID-19 mRNA vaccines.
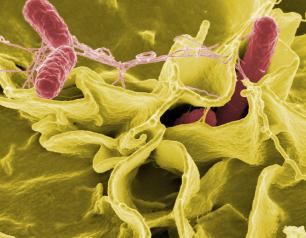
NIH Scientists Find that Salmonella Use Intestinal Epithelial Cells to Colonize the Gut
May 26, 2021
The immune system’s attempt to eliminate Salmonella bacteria from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract instead facilitates colonization of the intestinal tract and fecal shedding, according to National Institutes of Health scientists. The study, published in Cell Host & Microbe, was conducted by National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) scientists at Rocky Mountain Laboratories in Hamilton, Montana.

T Cells Recognize Recent SARS-CoV-2 Variants
March 30, 2021
When variants of SARS-CoV-2 (the virus that causes COVID-19) emerged in late 2020, concern arose that they might elude protective immune responses generated by prior infection or vaccination, potentially making re-infection more likely or vaccination less effective. To investigate this possibility, researchers from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health, and colleagues analyzed blood cell samples from 30 people who had contracted and recovered from COVID-19 prior to the emergence of virus variants.
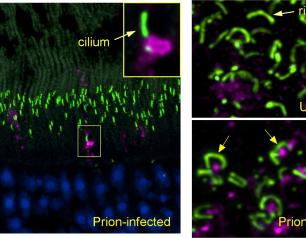
Scientists Identify Locations of Early Prion Protein Deposition in Retina
January 29, 2021
The earliest eye damage from prion disease takes place in the cone photoreceptor cells according to a new NIH study of prion protein accumulation.