TSE/Prion Biochemistry Section
Byron Caughey, Ph.D.
Chief, TSE/Prion Biochemistry Section

Major Areas of Research
- Prion diseases
- Alzheimer’s disease and other tauopathies
- Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies
- Prion structural biology and biochemistry
- Prion cell biology
- Diagnostic tests for pathological protein aggregates
- Prion disease therapeutics
Program Description
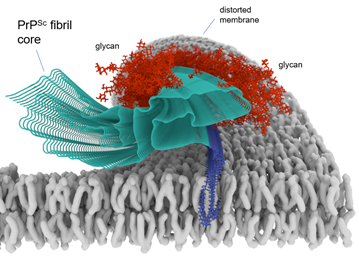
Cryo-EM-based infectious prion fibril core structure depicted in a membrane.
Many neurodegenerative diseases are caused by prion-like self-propagating aggregates of specific proteins such as tau (e.g., Alzheimer’s), α-synuclein (e.g., Parkinson’s), and PrP (prion diseases). We emphasize biochemical, structural biological, and cell biological studies of such pathological aggregates. For example, we have used cryo-electron microscopy to determine the first high-resolution structures of bona fide infectious PrP prions. We have exploited the self-propagating properties of proteopathic aggregates to develop ultrasensitive seed amplification assays (RT-QuIC assays) that are not only valuable in fundamental research, but also providing high diagnostic accuracy for prion diseases and synucleinopathies using clinically accessible biospecimens. Our tau RT-QuIC assays can detect and discriminate different pathological forms of tau aggregates with unprecedented sensitivity, and we are currently evaluating their diagnostic utility. We are also seeking to improve the practicality and quantitative precision of RT-QuIC assays. Armed with our new near-atomic prion structures, we are seeking new approaches to blocking prion growth and toxicity for therapeutic purposes against prion disease.

RT-QuIC comparison of nasal brushings (OM) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimens from human Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) vs non-CJD control patients.
Biography
Education
Ph.D., 1985, University of Wisconsin-Madison
Dr. Caughey received his Ph.D. in biochemistry from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in 1985 and completed postdoctoral studies in pharmacology at Duke University Medical Center from 1985 to 1986. He has conducted research on prions and other proteinopathies in the Laboratory of Persistent Viral Diseases (now Laboratory of Neurological Infections and Immunity) since 1986. He became a tenured senior investigator in 1994. Dr. Caughey is a Fellow of the American Academy of Microbiology.

Fluorescently tagged prions taken up and transported along neuritic projections in a cultured neuron.
Selected Publications
Alam P, Hoyt F, Artikis E, Soukup J, Hughson AG, Schwartz CL, Barbian K, Miller MW, Race B, Caughey B. Cryo-EM structure of a natural prion: chronic wasting disease fibrils from deer. Acta Neuropathol. 2024 Oct 24;148(1):56.
Vascellari S, Orrù CD, Groveman BR, Parveen S, Fenu G, Pisano G, Piga G, Serra G, Oppo V, Murgia D, Perra A, Angius F, Hughson AG, Haigh CL, Manzin A, Cossu G, Caughey B. α-Synuclein seeding activity in duodenum biopsies from Parkinson's disease patients. PLoS Pathog. 2023 Jun 30;19(6):e1011456.
Hoyt F, Standke HG, Artikis E, Schwartz CL, Hansen B, Li K, Hughson AG, Manca M, Thomas OR, Raymond GJ, Race B, Baron GS, Caughey B, Kraus A. Cryo-EM structure of anchorless RML prion reveals variations in shared motifs between distinct strains. Nat Commun. 2022 Jul 13;13(1):4005.
Kraus A, Hoyt F, Schwartz CL, Hansen B, Artikis E, Hughson AG, Raymond GJ, Race B, Baron GS, Caughey B. High-resolution structure and strain comparison of infectious mammalian prions. Mol Cell. 2021 Nov 4;81(21):4540-4551.e6.
Kraus A, Saijo E, Metrick MA 2nd, Newell K, Sigurdson CJ, Zanusso G, Ghetti B, Caughey B. Seeding selectivity and ultrasensitive detection of tau aggregate conformers of Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2019 Apr;137(4):585-598.
Zanusso G, Bongianni M, Caughey B. A test for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease using nasal brushings. N Engl J Med. 2014 Nov 6;371(19):1842-3.
Patents
Caughey WS, Caughey B, inventors; The United States of America as represented by the Department of Health and Human Services, assignee. Inhibitors of amyloid formation. United States patent US 6,632,808. 14 Oct 2003.
Chesebro BW, Caughey BW, Chabry J, Priola S, inventors; The United States of America as represented by the Department of Health and Human Services, assignee. Inhibitors of formation of protease resistant prion protein. United States patent US 6,355,610. 12 Mar 2002.
Chesebro BW, Caughey BW, Chabry J, Priola S, inventors; The United States of America as represented by the Department of Health and Human Services, assignee. Inhibitors of formation of protease resistant prion protein. United States patent US 6,211,149. 3 Apr 2001.
Caughey B, Race R, inventors; The United States of America as represented by the Department of Health, assignee. Inhibition of diseases associated with amyloid formation. United States patent US 5,276,059. 4 Jan 1994.
Caughey BW, Atarashi R, Moore RA. US Patent 8,216,788. Detection of infectious prion protein by seeded conversion of recombinant prion protein. July 10, 2012.
Caughey BW, Atarashi R, Moore RA. European Patent EP 2554996. Detection of infectious prion protein by seeded conversion of recombinant prion protein. September 3, 2014.
Caughey, Byron Winslow, Groveman, Bradley Richard, Groveman Christina Doriana, Raymond, Lynne DePuma, Hughson, Andrew Gregory; The United States of America, as represented by the Secretary, Department of Health and Human Services, assignees. Assay For The Detection Of Alpha-synuclein Seeding Activity Associated With Synucleinopathies. United States patent US 11,313,867 B2. 26 April 2022.
Audio
CJD Foundation support group teleconference interview
Videos
This Week in Virology: Rocky Mountain Virology
Research Group
We address prion-like self-propagating aggregates of specific proteins such as tau (Alzheimer’s), α-synuclein (Parkinson’s), and PrP (prion diseases) with biochemical, structural biological, and cell biological studies. Armed with our new near-atomic prion structures, we seek new approaches to blocking prion growth and toxicity for the treatment of prion disease.


