The drug screening team tests and characterizes novel compounds, drugs, and antibodies against numerous viruses in multiple cell lines under a variety of conditions. Compounds are evaluated in cell-based assays for inhibition of viral replication and reduction of virus yields, plaques, or cytopathic effect. In addition, recombinant reporter gene viruses are available as tools for antiviral screening.
Main Areas of Focus
The drug screening laboratory supports the testing of compounds for the potential treatment of infections with high-consequence viral pathogens and reemerging viruses of significant public-health concern. The compounds are tested with cell-based assays, and the resulting data are used to decide whether further studies in animal models of infection are warranted. In addition, scientists in the drug screening laboratory have expertise in developing and implementing novel assays for specific viruses of interest.
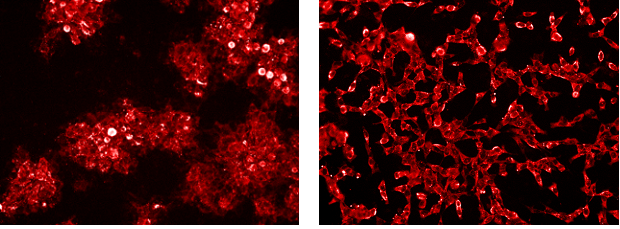
Left: Vero E6 cells infected with Ebola virus (EBOV), isolate Makona, stained with mouse anti-EBOV VP40 (AE11) primary antibody and goat-anti-mouse-Alexa 594 secondary antibody. Right: Vero E6 cells infected with Lassa virus (LASV), strain Josiah, stained with mouse anti-LASV primary antibody and goat-anti-mouse-Alexa 594 secondary antibody.
Capabilities and Specialized Equipment
- Virus-specific antibodies for detection of infected cells
- Recombinant reporter gene viruses
- Virus yield reduction assay
- Plaque reduction assay
- Cytopathic effect (CPE) reduction assay
- High-throughput screening assays for:
- Ebola virus (EBOV)
- Marburg virus (MARV)
- Lassa virus (LASV)
- Junín virus (JUNV)
- Guanarito virus (GTOV)
- Machupo virus (MACV)
- Nipah virus (NiV)
- Human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV)
- Vaccinia virus (VACV): VACV-GFP
- Cowpox virus (CPXV): CPXV-GFP
- Mpox virus (MPXV): MPXV-GFP
- Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV)
- Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)
- Chemiluminescence
- Fluorescence
- Equipment:
- Tecan M1000 or Spark 20M plate reader
- Tecan M1000 or Spark 20M plate reader
- Operetta high-content imaging system
- Tecan D300e digital dispenser
- Multidrop Combi
- Integra VIAFLO 384-channel electronic pipette system
- Integra Assist Plus pipetting robot for full workflow automation
- Microplate washer

Tecan D300e Digital Dispenser allows rapid delivery to assay plates.

Integra VIAFLO 384-channel electronic pipette system provides the ability to dispense to a high volume of wells, increasing the number of plates that can be included in an assay.
Location
Integrated Research Facility at Fort Detrick (IRF-Frederick)
Contact Information
Jens H. Kuhn, M.D., Ph.D., Ph.D., M.S.
Principal Scientist and Director of Virology (Contractor)
IRF-Frederick
Standards
All procedures are well-documented and adhere to standard operating procedures (SOPs), methods, or study-approved plans and agreements.
Collaboration Opportunities
- Studies relevant to human disease
- Use of surrogate systems to test clinical hypotheses
- Use of biological systems to answer questions regarding disease pathogenesis and strategies for intervention including antimicrobials, vaccines, and other countermeasures
- Developing and incorporating cutting-edge technologies to understand infectious diseases
Read more about how to work with the IRF-Frederick.

